Digital Signature vs Physical Signature – Understanding Their Legal Validity.
DIGITAL SIGNATURE VS PHYSICAL SIGNATURE: WHICH HOLDS MORE LEGAL WEIGHT?
| In today’s fast-paced digital economy, contracts are increasingly signed online. But a pressing question still remains: Are digital signatures as legally binding as physical ones? Whether you’re a business owner, legal consultant, or freelancer, understanding the legal weight of each type of signature is essential. In this guide, we break down the key differences, legal standing, and security implications of digital and physical signatures—so you can confidently choose the right option for your agreements. |
What Is a Physical Signature?
A physical (wet) signature is the traditional handwritten signature used to approve documents. It’s usually signed with a pen on a hard copy and has long been considered the standard method of executing agreements.
Advantages:
- Tangible proof of intent
- Universally accepted
- Easy to produce in face-to-face meetings
Drawbacks:
- Easily forged
- Requires in-person presence or shipping
- Vulnerable to loss or damage
What Is a Digital Signature?
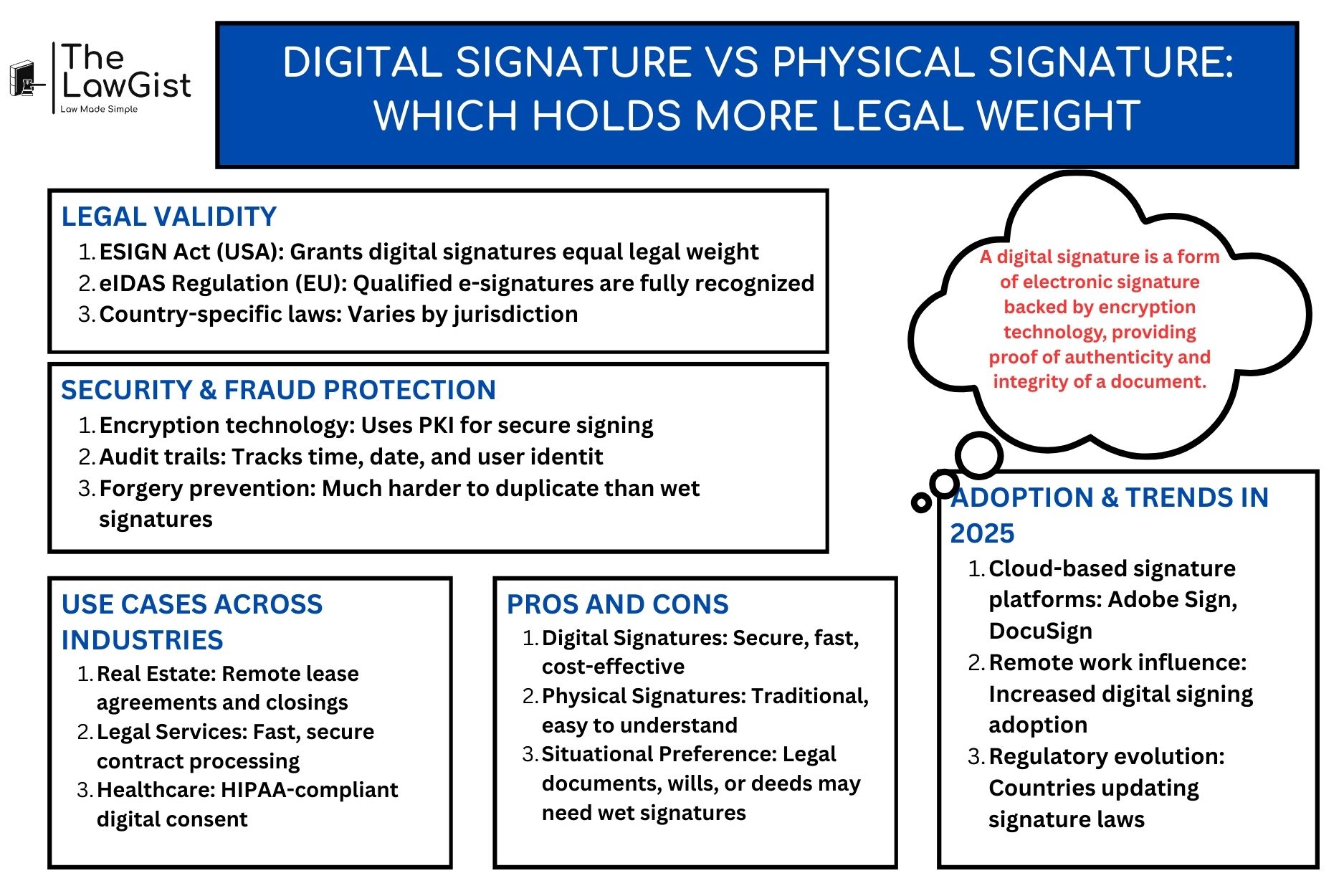
A digital signature is a form of electronic signature backed by encryption technology, providing proof of authenticity and integrity of a document. It’s commonly used in software like DocuSign, Adobe Sign, or HelloSign.
Key Features:
- Cryptographic security using public key infrastructure (PKI)
- Tamper-evident audit trails
- Authentication through digital certificates
Legal Weight: Digital vs Physical Signature
Global Recognition of Digital Signatures
Digital signatures are legally valid in most jurisdictions under specific regulations:
- United States: Under the ESIGN Act (2000) and UETA, digital signatures are legally enforceable.
- European Union: The eIDAS Regulation grants qualified digital signatures the same legal effect as handwritten ones.
- India: The Information Technology Act (2000) recognizes digital signatures backed by a certifying authority.
When Digital Signatures Hold More Weight
- Tamper-proof and time-stamped: Digital signatures offer more secure verification methods compared to physical signatures.
- Authentication and non-repudiation: You can verify the identity of the signer and ensure the document hasn’t been altered.
- Court admissibility: In many legal cases, a digital signature with a full audit trail has more evidentiary value than a physical one that can be easily forged.
When Physical Signatures May Be Preferred
- Notarized or witnessed documents: Some jurisdictions require in-person verification for wills, deeds, or marriage contracts.
- Documents executed in countries with outdated digital laws: In some regions, the legal framework may still prioritize handwritten signatures.
Security Comparison
| Criteria | Digital Signature | Physical Signature |
| Forgery Protection | High (Encryption, Digital Certificates) | Low (Easily forged or duplicated) |
| Audit Trail | Yes (Metadata, IP, Timestamp) | No |
| Remote Signing | Yes | No |
| Identity Verification | Strong (2FA, Biometrics in some cases) | Weak |
Industries Benefiting Most from Digital Signatures
- Real Estate: Remote signing of lease agreements and contracts
- Legal Firms: Secure client documentation and contracts
- Finance: Paperless account openings and loan approvals
- Healthcare: HIPAA-compliant consent forms and approvals
- Freelancers/Agencies: Streamlined service agreements and NDAs
Final Verdict: Which Holds More Legal Weight?
In most modern legal systems, **digital signatures hold equal or greater legal weight compared to physical signatures—provided they comply with local e-signature laws and use robust verification mechanisms. Always use certified e-signature platforms that offer legal compliance, encryption, and audit trails for maximum protection and enforceability.
Sources:
Also Read – ELECTRONIC RECORDS AND ELECTRONIC SIGNATURES
Frequently Asked Questions
- Are scanned signatures legally binding?
Yes, but they are considered electronic, not digital, and offer lower security and authenticity than digital signatures.
2. Is a digital signature safe for contracts?
Yes, especially if it’s created using a certified digital signature platform with encryption and audit trail features.
3. Can a digital signature be forged?
While nothing is 100% forgery-proof, digital signatures are exponentially harder to forge than physical ones due to encryption and identity verification.







