From pollution control to GST disputes and voter roll reforms — India’s top courts are reshaping environmental, tax, and electoral laws through crucial judicial rulings.
DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS (24 OCTOBER 2025)
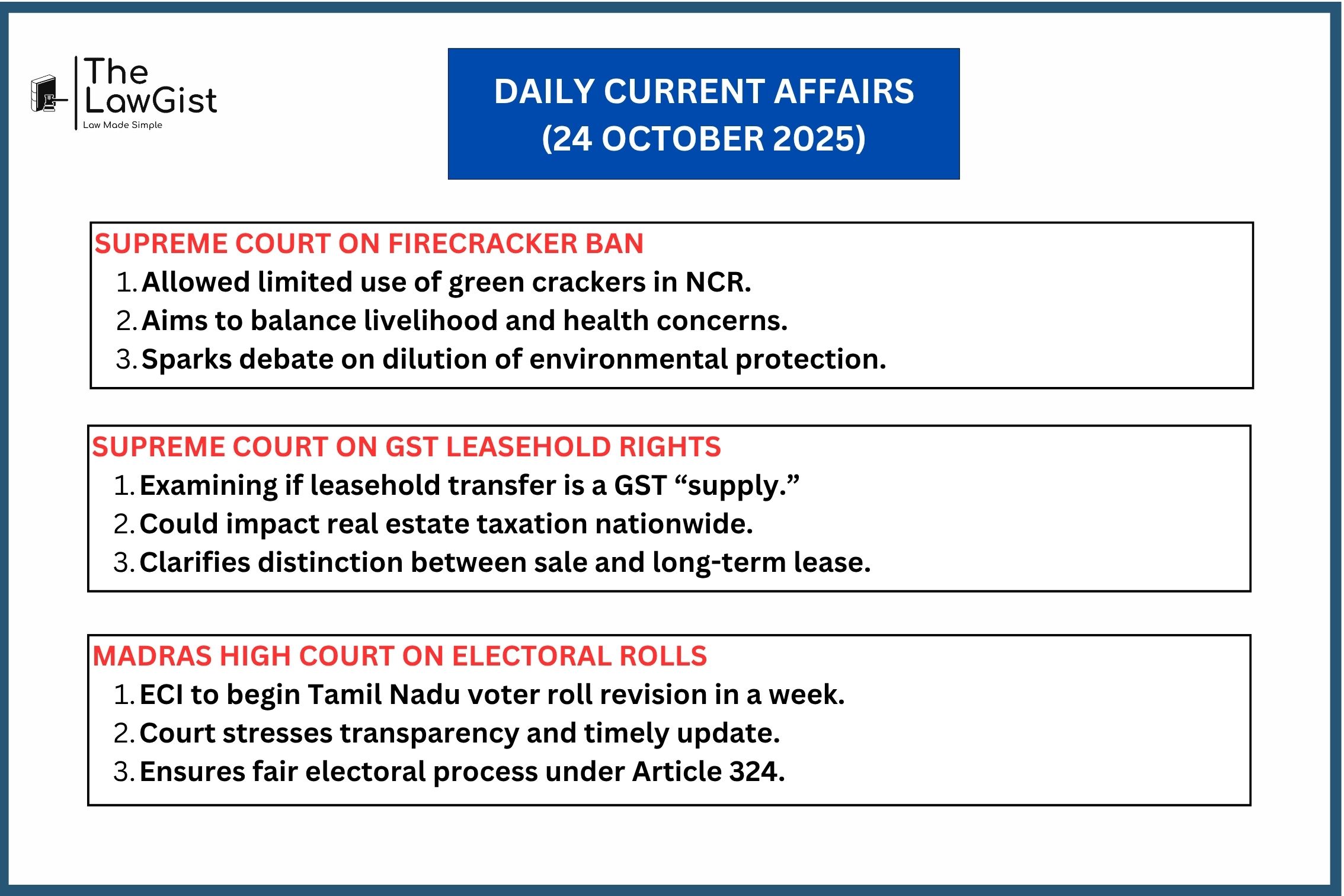
SUPREME COURT’S ORDER DILUTING FIRECRACKER BAN IN NCR SPARKS QUESTIONS
Case Overview: Supreme decision on firecracker ban.
The Supreme Court recently allowed the use of “green crackers” in NCR, relaxing its earlier complete ban. Critics argue this move undermines years of environmental jurisprudence on air pollution control. The Court emphasized balancing livelihood rights of traders with public health and environmental protection.
Legal Provisions
- Article 21 – Right to Life (including clean environment)
- Article 48A – Protection of environment
- Environment (Protection) Act, 1986
- Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981
- Previous SC judgments: Arjun Gopal vs. Union of India (2018)
Source: Supreme Court of India
SUPREME COURT EXAMINES WHETHER TRANSFER OF LEASEHOLD RIGHTS ATTRACTS GST
The Supreme Court is examining if the transfer of leasehold rights in land qualifies as a “supply” under GST. The bench highlighted the need to distinguish between sale and long-term lease transactions to avoid double taxation. The outcome could significantly impact real estate and industrial lease agreements.
Legal Provision:
- Article 246A – Concurrent power to levy GST
- Section 7, Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Act, 2017 – Definition of “supply”
- Schedule III, CGST Act – Transactions neither treated as supply of goods nor services
- Article 265 – No tax without authority of law
Source: Supreme Court of India
ECI TO BEGIN ELECTORAL ROLL REVISION IN TAMIL NADU WITHIN A WEEK: MADRAS HIGH COURT TOLD
Case Name: B Sathyanarayanan vs. The Chief Election Commissioner and Another WP 39744 of 2025
The Election Commission of India informed the Madras High Court that revision of Tamil Nadu’s electoral rolls will start within a week. The submission came amid concerns about irregularities and outdated voter data. The Court directed close monitoring to ensure free, fair, and transparent elections.
Legal Provision:
- Article 324 – Powers of Election Commission
- Representation of the People Act, 1950 – Preparation and revision of electoral rolls
- Representation of the People Act, 1951 – Conduct of elections
- Article 14 – Right to equality in electoral participation
Source: Supreme Court of India
Also Read: SC TRANSFERS EUREKA FORBES PATENT SUIT TO BOMBAY HIGH COURT IN ATOMBERG CASE