Supreme Court delivers key rulings on equality in employment, limits of anticipatory bail hearings, and the scope of witness protection versus bail cancellation.
DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS (05 SEPTEMBER 2025)
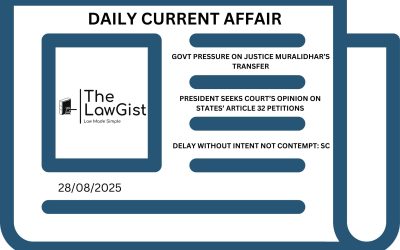
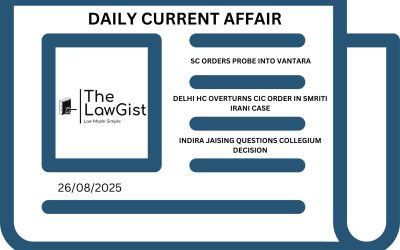
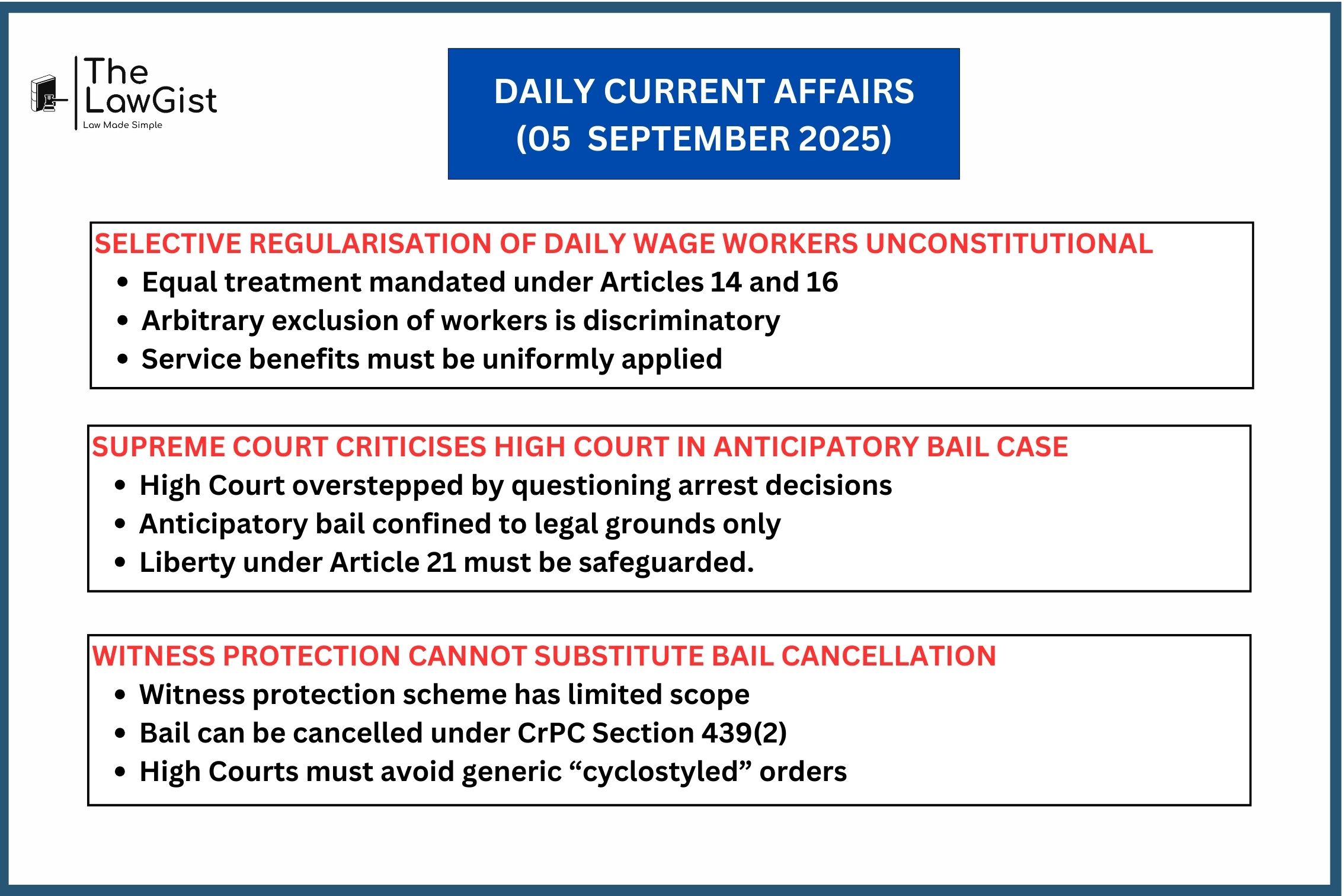
SELECTIVE REGULARISATION OF DAILY WAGE WORKERS UNCONSTITUTIONAL: SUPREME COURT
Case Name: DHARAM SINGH & ORS. …APPELLANT(S) vs. STATE OF U.P. & ANR. …RESPONDENT(S)
The Supreme Court held that selectively granting regular employment benefits to only some daily wage workers in the same establishment violates constitutional guarantees. The Court emphasized that all employees similarly situated must be treated equally, and any arbitrary differentiation amounts to discrimination.
Legal Framework:
- Article 14, Constitution of India – Prohibits arbitrary state action
- Article 16, Constitution of India – Ensures equal opportunity in public employment
- Service Law Principles – Equal treatment of employees performing similar work
Source: Supreme Court of India
APEX COURT CRITICISES HIGH COURT FOR OVERSTEPPING IN ANTICIPATORY BAIL CASE
Case Name: GURSEWAK SINGH Petitioner(s) vs. STATE OF PUNJAB Respondent(s)
The Supreme Court rebuked the Kerala High Court for asking why the accused was not arrested, instead of addressing the merits of his anticipatory bail plea. The Court clarified that bail adjudication should remain within the legal framework and not intrude upon the domain of investigation.
Legal Framework:
- Section 438, CrPC, 1973 – Provision for anticipatory bail
- Article 21, Constitution of India – Protects liberty from arbitrary arrest
- Judicial Precedent – Courts must confine bail hearings to legal considerations
Source: Supreme Court of India
SUPREME COURT: WITNESS PROTECTION IS NO SUBSTITUTE FOR BAIL CANCELLATION
Case Name: PHIRERAM …APPELLANT(S) vs. STATE OF UTTAR PRADESH & ANR. …RESPONDENT(S)
The Supreme Court held that placing witnesses under protection cannot replace cancellation of bail if circumstances justify such relief. The Court also condemned the Allahabad High Court’s practice of issuing “cyclostyled” orders without applying judicial reasoning, stressing that each bail matter requires independent evaluation.
Legal Framework
- Section 439(2), CrPC, 1973 – Power to cancel bail
- Witness Protection Scheme, 2018 – Meant to safeguard witnesses, not override bail law
- Article 21, Constitution of India – Guarantees fair trial and due process
Source: Supreme Court of India
Also Read: DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS (04 SEPTEMBER 2025)